This specification of the Web service interface for consent verification describes the Web services that consent verification offers health professionals and citizens respectively, who through the user will perform verification of consents.
A consent describes a relationship between:
a citizen,
(what) information about the citizen
(who) health professional persons or organizations in addition to their entry way to the information
For a detailed description of the data model for consents and the structure of consent elements, see [Datamodel].
A negative consent means that the citizen has declined that retrieval or disclosure of sensitive data (what) can be accomplished by an identified target group (who).
A positive consent selectively allows that an identified target group (who) can retrieve sensitive data (what), despite one or more negative consents for the sensitive data. A positive consent can furthermore be used in external systems to allow identified target group to retrieve sensitive data that has been marked externally as private.
A consent is either active or inactive. An active consent can affect a health professional’s access to sensitive data about the citizen. An inactive consent has no impact, but is a record of a formerly active consent, that the citizen has nullified.
A consent can be attached with a validity period (when), that states a period for which a health professional’s access to the information may be restricted (on negative consent) or relaxed (on positive consent). The consent’s validity period concerns the time for desired retrieval of information only; it does not concern when the information was created or registered. Positive consents must be attached with a validity period, while negative consents only requires a stated start date.
A health professional’s access to sensitive data concerning a citizen is unaffected by a consent if the health professional is outside the consent’s field of action. This is the case if for instance a negative consent concerns another specific health professional.
The purpose of this section is to provide an overview of the definitions and documents references used in this document.
| Definition | Description |
|---|---|
NSI | National eHealth Authority |
NSP | National Service Platform (within health care) |
SAML | Security Assertion Markup Language |
STS | Security Token Service |
NCP | National Contact Point |
| Reference | Description |
|---|---|
OIO-NDR | OIO Navngivnings- og Designregler, OIO-NDR version 3.2, http://www.itst.dk/it-arkitektur-og-standarder/standardisering/datastandardisering/oioxml-udvikling/regler/ndr-3.2 |
DGWS 1.0 | Den Gode Webservice 1.0 |
DGWS 1.0.1 | Den Gode Webservice 1.0.1 |
HSUID-Header | Healthcare Service User Identification Header (SSE/11734/IFS/0018) |
OIO-WSDL | Guideline for development and use of OIOWSDL, http://www.itst.dk/it-arkitektur-og-standarder/standardisering/standarder-for-serviceorienteret-infrastruktur/standarder-for-webservices/filer-til-standarder-for-webservices/OIOWSDL_english.pdf |
In the document, the concepts of authorization and authorized are used primarily in a security context, that is, in the understanding that a person or a system is authorized to use a given resource. If the concepts are applied towards health professionals with Danish authorization listed in Danish Health Authority’s authorization register, it will be stated explicitly.
A system that uses Web services described in this document is referred to as a user system.
It is assumed that the reader understands the general use of SOAP-based Web services, why technical terms such as SOAP, WSDL etc. are not clarified. Knowing Den Gode Webservice (DGWS) 1.0.1 described in [DGWS 1.0] and [DGWS 1.0.1] will facilitate comprehension considerably.
| Version | Date | Responsible | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
0.1 | 24.4.2012 | Systematic | Initial version. |
0.2 | 1.5.2012 | Systematic | Optimization of data elements by verification of consent for data elements. Addition of ConsentForForeignerCheck operation. |
0.9 | 14.5.2012 | Systematic | HSUID-header reference added, reading guide updated, web service semantics updated. |
1.0 | 29.6.2012 | Systematic | ConsentForForeignersCheck, SOAP-faults, table elaboration, general improvements. |
1.1 | 28.11.2014 | Systematic | References to National Patient Index (NPI) removed. |
1.2 | 09.09.2016 | Systematic | Changed nsi:skscode to nsi:skskode and nsi:sorcode to nsi:sor to fit XML schema |
1.3 | 13.06.2018 | Systematic | Migrated to NSPOP SVN |
| 22.10.2018 | KIT | Document moved from Word to Confluence. Original document name was: IFS0014 Consent Verification Service Interface Description.docx |
The following section describes the usage scenarios that the Web service for consent verification supports.
A health professional can check a citizen’s consent registrations to determine if a consent exist that blocks the health professional’s access to the citizen’s data. This usage scenario is supported by the operation ConsentForUserCheck. The check will typically be performed before retrieving information about the citizen.
The result of the operation is a statement about whether the health professional has consent for the citizen’s information in the form of negative, positive or DataSpecificConsent.
A result in the form of DataSpecificConsent means that one or more consents exists on selected information concerning the citizen. Thus, it is not possible to decide if the health professional has consent for all information concerning the citizen. Consequently, additional consent verification of the individual data elements must be performed before the health professional can be presented with information concerning the citizen. On positive reply, no further verification of data is performed. On negative reply, all information concerning the citizen is unavailable for the health professional.
A health professional desires to retrieve a number of informations about a citizen. A previous call of the operation ConsentForUserCheck returned the result DataSpecificConsent. Thus, it is necessary to check each individual data element for citizen’s consent in regard to the health professional. When the user system has obtained the list of data elements concerning the citizen, this usage scenario is supported by the operation ConsentForUserCheck.
The result of the operation is a list of data elements for which the health professional has consent.
A foreign health professional desires to retrieve information concerning a Danish citizen. This happens through a call from another country’s NCP to the Danish NCP. Before the Danish NCP returns the information about the concerned Danish citizen to another country’s NCP, the Danish NCP verifies that the citizen has registered a positive consent for foreign health professionals by calling the operation ConsentForForeignersCheck.
The result of the operation is a statement on whether foreign health professionals has positive consent for the citizen’s information.
The template below documents the operations that are offered by the consent verification Web service. The most important elements for input and output are described in section 5.
Name: <operation header> | |
|---|---|
Description: | Description of the functions purpose. |
Input: | Input parameters. |
Output: | Output parameters. |
Error handling: | Description of error handling, typically refers to the general description of error handling in (section 4.7). |
Roles: | Description of necessary roles. |
Prerequisites: | Description of prerequisites that must be met for the function to complete successfully. |
The operations below are available on the verification service.
Name: ConsentForUserCheck | |
|---|---|
Description: | Examines whether a citizen has expressed general positive, general negative or data specific consent towards the user. |
Input: | ConsentForUserCheckRequest which consists of: PatientPersonCivilRegistrationIdentifier Identification of the citizen for which consent is desired examined. HealthcareProfessionalIdentifier HealthcareProfessionalIdentifierOnBehalfOf HealthcareProfessionalOrganization |
Output: | ConsentForUserCheckResponse which consists of: ConsentIndication the states consent for health professional or organization on the form: Positive – means that specific content has been given by the citizen to the concerned health professional or the organization affiliated with the person in question. Negative – means that the health professional does not have access to the citizen’s data. DataSpecificConsent – means that consent exists for specific data, so that it is not possible to decide from the health professional and affiliated organisation alone whether access is possible. Consequently, it is necessary to check consent on the basis of the data the health professionals desires presented. |
Error handling: | See section 4.7. |
Roles: | Health professional. |
Prerequisites: | Both user system and user must be authenticated and authorized as described in section 4.2.1. |
Name: ConsentForDataCheck | |
|---|---|
Description: | Examines whether a citizen has expressed positive or negative consent in regard to the user towards a number of specific data elements. |
Input: | ConsentForDataCheckRequest which consists of: PatientPersonCivilRegistrationIdentifier Identification of which citizen for which consent is desired examined. HealthcareProfessionalIdentifier HealthcareProfessionalIdentifierOnBehalfOf HealthcareProfessionalOrganization ConsentForDataRegistrations |
Output: | ConsentForDataCheckResponse which consists of: PositiveConsentDataRegistrations Collection of document ID’s from ConsentForDataRegistrations input, where positive consent has been given concerning the health professional. |
Error handling: | See section 4.7. |
Roles: | Health professional |
Prerequisites: | Both user system and user must be authenticated and authorized as described in section 4.2.1. |
Name: ConsentForForeignersCheck | |
|---|---|
Description: | Examines if the citizen has given positive consent for foreign health professionals to access the citizens’ health information. |
Input: | ConsentForForeignersCheckRequest which consists of: PatientPersonCivilRegistrationIdentifier Identification of the citizen for which consent is desired examined. |
Output: | ConsentForForeignerCheckResponse which consists of: ConsentForForeigners which state consent for foreign health professionals Positive – means that specific consent has been given for foreign health professionals to access the citizens’ information. Negative - means that foreign health professionals do not have access to the citizen’s information. |
Error handling: | See section 4.7. |
Roles: | Health professional |
Prerequisites: | Both user system and user must be authenticated and authorized as described in section 4.2.1. |
The Web service expects SOAP messages, where the SOAP header contains security header and Medcom header as required by DGWS 1.0.1, in addition to a Healthcare Service User Identification (HSUID) header.
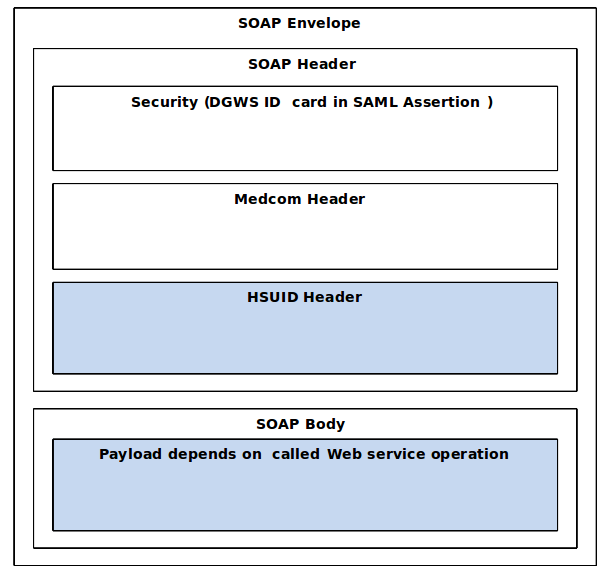
Figure 1 SOAP message containing security header, Medcom header and HSUID header is used as message format.
The format of Security and Medcom headers are described in [DGWS 1.0] and [DGWS 1.0.1], while the format of the HSUID header is described in [HSUID-Header].
When the user of the service is a health professional, attributes in Table 1 are applied in the HSUID-header.
| The element Attribute | Subelement AttributeValue | |
|---|---|---|
Name-attribute | NameFormat-attribute | - |
nsi:UserType | nsi:HealthcareProfessional | |
nsi:ActingUserCivilRegistrationNumber | The health professional’s social security number | |
nsi:OrgUsingID | nsi:sor or nsi:skskode or nsi:ynumber | Identification of the organization that the health professional is affiliated with as user. The attribute must be present at least once and may occur twice. With two occurrences, the organization can be identified by SOR-code and for instance SHAK-code. |
nsi:ResponsibleUserCivilRegistrationNumber | Social security number of the health professional under whose responsibility the user acts. If this is the same person as the user, the same social security number is given. | |
nsi:ResponsibleUserAuthorizationCode | Authorization number listed in the National Board of Health authorization register for the health professional under whose responsibility the user acts. If the user is a health professional without authorization number listed in the National Board of Health authorization register not working under the responsibility of a designated health person, e.g., a paramedic with special competence, the value "-" is indicated. | |
nsi:SystemOwnerName | Name of the system owner of the user system | |
nsi:SystemName | Name of the user system | |
nsi:SystemVersion | Version of the user system | |
nsi:OrgResponsibleName | Name of the organization responsible for operation of the user system. | |
Table 1 Attributes in the HSUID-header applied for user who is a health professional.
The identification of the organization for which the user is associated, may be provided as a single value and a single format, such as SHAK-code:
<hsuid:Attribute Name="nsi:OrgUsingID" NameFormat="nsi:skskode"> <hsuid:AttributeValue>6620151</hsuid:AttributeValue> </hsuid:Attribute> |
Alternatively, the organization, to which the user is affiliated, can be specified by two values, e.g. as both SOR- and SHAK-code:
<hsuid:Attribute Name="nsi:OrgUsingID" NameFormat="nsi:sor"> <hsuid:AttributeValue>440081000016006</hsuid:AttributeValue> </hsuid:Attribute> <hsuid:Attribute Name="nsi:OrgUsingID" NameFormat="nsi:skskode"> <hsuid:AttributeValue>6620151</hsuid:AttributeValue> </hsuid:Attribute> |
Note that it is the consumer system's responsibility to ensure that there is consistency between the given ID across SOR, SHAK and Healthcare Provider Number (Danish: ydernummer) classification systems.
The security of this Web service is based on the SOSI integration pattern in Den Gode Webservice (DGWS). Authentication is carried out by a trusted third party component on NSP (Security Token Service) and based on OCES digital certificates. As a rule, the service requires authentication with the STS component based on employee signature (MOCES). However, highly trusted systems - initially only Health journal - can during a transitional period gain access by level 3 based on company signature (VOCES).
Additional security aspects, including authorization, integrity, confidentiality, availability and privacy considerations are enforced to only some extent by the technical service. The aspects that are not currently handled by the technical service will be handled in the service agreement, as specified by the data-responsible authority (NSI), which consumers of the service must agree to.
When STS’ signature of the ID card has been validated successfully, then the consumer has been authenticated.
Authorization of consumer system is performed using a whitelist in the web service based on information in the system-part of the ID card.
When the user system is authenticated and authorized, the user is authenticated by the HSUID header attribute nsi: ActingUserCivilRegistrationNumber.
Whether the user is health professional or citizen is determined from the HSUID header attribute nsi: UserType.
Web service-operation(s), where the user is health professional
The Web service authorizes all users who are health professionals to use its operations.
A request with ID card is rejected when it has been more than 24 hours since the beginning of the ID card validity period.
As required by DGWS 1.0.1, only HTTP-status codes 200 and 500 are used.
On HTTP status code 200 FlowStatus is always flow_finalized_succesfully.
Timeout on web service-operations is the same as default timeout on the NSP platform.
Each request is handled in its own session.
No check is performed whether MessageID in request has been received previously and no answer is guaranteed if a request with the same MessageID is received.
This deviates from DGWS 1.0.1 in regard to handling of retransmission.
If the request contains a flow ID, it is reused in the reply. Handling of flow ID complies with DGWS 1.0.1.
Digital signing of replies is not supported. On request for non-repudiation, a fault-error message is returned as described in [DGWS 1.0].
SOAP errors are returned with the components as described hereinafter. A structure has been chosen wherein both standard error codes as described in [DGWS 1.0] and service specific error codes can be returned.
<soap:Body>
<soap:Fault>
<faultcode>soap:Server</faultcode>
<faultstring>Description of the error</faultstring>
<detail>
<FaultInfo xsi:type="ns2:dgwsInfo" xmlns="urn:dk:nsi:consent:verification:service:1" xmlns:ns2="http://www.medcom.dk/dgws/2006/04/dgws-1.0.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<ns2:FaultCode>expired_idcard</ns2:FaultCode>
</FaultInfo>
</detail>
</soap:Fault>
</soap:Body> |
Code listing 1 Structure of SOAP faults returned from Web service operation. The example shows FaultCode used when the ID card has expired.
For all web service operations described in section 3 will be used SOAP Fault with FaultCode-values as listed in Table 2, originating from DGWS 1.0.1.
FaultCode | Description |
|---|---|
missing_required_header | One or more mandatory DGWS headers are missing in the enclosed message, e.g. ID card, which always must be provided. |
security_level_failed | Authentication or authorization error. Invalid choice of security level. |
invalid_idcard | Authentication or authorization error. Error in SOSI ID card. |
invalid_certificate | Authentication or authorization error. Certificate is not OCES or expired. |
expired_idcard | Authentication or authorization error. SOSI ID expired or too old for this Web service provider. |
not_authorized | User has insufficient rights to perform the Web service operation call. E.g., company registration number is not on whitelist. |
nonrepudiation_not_supported | Web service provider system cannot perform a digital signature on the reply. |
Table 2 Applied FaultCode-values originating from DGWS 1.0.1
Additionally, service specific FaultCode values as listed in Table 3 are used.
FaultCode | Description |
|---|---|
consent_service.ConsentDatabase | An internal server error has occurred in connection with consent database communication |
consent_service.SORLookup | An internal server error has occurred in connection with lookup in the SOR-table |
consent_service.ServiceInvocation | The service was called with invalid parameters: |
invalid_date_timezone | An attached date has invalid format, cf. DGWS 1.0.1. |
consent_service.UnknownError | An unknown server error resulted in failed call |
Table 3 Applied service-specific FaultCode-values
The WSDL that describes the Web service described in this document does not specify the SOAP Fault status codes for every operation.
It is validated that:
Properly formatted HSUID header is included in the SOAP header, including the attributes that respectively may and must be present for a given user type as described in section 4.1.1. Furthermore, it is validated that attribute values belong to established value sets and is not null or simply whitespaces
ID card in security header is valid and signed by STS and that the additional conditions described in section 4.2 are met
There will be performed:
No XML schema validation
No validation that stated authorization numbers are valid and found in National Board of Health authorization register
No validation that there is consistency between the health professional’s organization ID's when multiple ID and classification systems are provided.
No validation that a health care professional is affiliated with stated organization
No validation that the user is acting under responsibility of stated health professional
Consent verification service is based on the following standards:
SOAP version 1.1
Soap Fault version 1.1
WS-I Basic Profile 1.1
OIO namegivnings- og designregler
DGWS 1.0.1, with the exception of requirements regarding retransmission and control of reuse of messageID as described in section 4.5, and with the exception of structure used on errors as described in section 4.7.1.
This section provides a general description of the key elements in the XML schemas, which together with WSDL files define the Web service operations described in 3.2. Additionally, cardinality is provided when an element is not compulsory.
Element-name | Description |
HeathcareProfessionalIdentifierOnBehalfOf | Identification of the health professional who is acted on behalf of. The field is optional and can be provided without content. |
Element-name | Description |
ConsentDataRegistration[0..n] | Collection of data elements where consent must be verified. |
Element-name | Description |
Identifier[1] | Unique identification of data element (key value) as provided by the calling system. |
Origin[1] | SOR, SHAK or provider-number which states the origin of the data element |
CreationDateTime[1] | Time for creation of data element in question |
Element-name | Description |
ConsentIndication | Positive, negative or applicable to specific data. With value set: Positive, Negative, DataSpecificConsent |
Element-name | Description |
DataIdentifiers[0..n] | Collection of unique identification of data element (key-value) as provided by the calling system |
Element-name | Description |
ConsentForForeigners | Positive or negative with value set: Positive, Negative |
For the consent verification, the interface between the actor systems and consent verification is versioned.
The interface specification constitutes the contract that defines how the systems involved must act.
The interface specification consists of:
the technical specification of schemas and service descriptions (documented as a WSDL file, see section 7)
documentation of the semantic and functional meaning of data that is exchanged (documented in this document).
As part of the WSDL for ConsentVerification figures headers that are defined and versioned elsewhere. The body is specific for ConsentVerification and follows the naming
”urn:dk:nsi:consentservices:verification:service:<version>”
where the version changes on redefinition of the ConsentVerification interface.
WSDL for the service can be obtained by runtime WSDL-generation towards a deployed service. If the service in NSP test environment cannot be accessed with a view to runtime WSDL-generation, then a locally built and deployed service can be used.